서 론
연하장애 치료에는 보상전략(compensatory strategies), 재활치료 기법(rehabilitation techniques), 신경근전기 자극(neuromuscular electrical stimulation) 등의 방법 이 있다(Jung & Park, 2015). 보상전략은 안전하게 삼 킬 수 있도록 음식물이 흐르는 경로를 효과적으로 변형시 켜 주는 방법이다. 이 방법은 자세변화, 메뉴버, 음식덩이 의 크기, 점도, 온도, 맛을 적절하게 변화시키는 것이다 (송영진 등, 2007). 재활치료 기법은 반복적인 자극과 운동으로 삼키기 매커니즘의 생리기전을 변화시켜 기질 상에서의 영구적인 변화를 이끌어내는 중재기법이다. 이 방법에는 자극 치료와 운동 치료가 있다(송영진 등, 2007). 기본원리는 이상반사의 억제와 삼킴반사의 촉진 이며, 구강 및 안면부의 감각자극, 구강 및 인후근육의 강화운동, 움직임 범위와 근력 향상, 비정상적인 근육의 긴장도를 감소시키는 것이다(Kim, Choi, & Kim; 1994). 신경근전기자극은 삼킴 근육의 기능적 근수축 패턴을 재교 육 시킨다(Heijnen, Speyer, Baijens, & Bogaardt, 2012). 여러 연구에서 신경근전기자극이 연하장애 환자의 운동 피질을 재구성하여, 구강인두 근육의 근력을 강화시킬 뿐만 아니라 신경가소성을 촉진시킨다고 하였다(Carnaby-Mann & Crary, 2007; Fraser et al., 2003; Hamdy et al,, 2003). 뇌졸중 환자를 대상으로 수행한 연하장애 치료에 관한 최신의 연구를 살펴보면, 전통적인 연하재활치료와 새로운 치료기법을 함께 적용하여 연하재활치료의 효과를 극대화하려고 한다. 새로운 치료기법으로는 신경근 전기 자극, 근전도 유발 전기자극(Electeomyogramtriggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation; EMG-NMES), 상상훈련(mental imagery training), 경두개 직류자극 기(transcranial Direct Current Stimulation; tDCS), 경두개 자기자극기(repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation; rTMS), 인두 전기 자극기(Pharyngeal Electrical Stimulation; PES), 기능적 자기 자극기 (Functional Magnetic Stimulation; FMS) 등이 있다.
연하재활치료는 오랫동안 보상전략과 재활치료 기법 에 의존했으나, 최근에 개발된 다양한 기술들이 연하재 활치료에 적용되고 있다. 연하장애를 보이는 뇌졸중 환 자들의 임상 증상, 치료법, 예후에 영향을 줄 수 있는 병 변, 발병 시기 등의 요인들이 최신 연구에서 어떻게 반영 되고 제시되고 있는지를 알아보고, 이를 근거로 임상 치 료에 적용하는 것은 매우 중요한 일이다.
이에 본 연구에서는 체계적 문헌고찰을 통해 뇌졸중 환자를 대상으로 한 최근 연구에서 제시된 치료 방법들 을 치료의 효과와 각 연하장애 증상별로 재정리하고자 한다. 이를 통하여 작업치료사들이 환자의 특성에 맞는 효과적인 연하재활치료를 선택할 수 있도록 근거 자료를 제공하고자 한다.
연구 방법
2문헌검색전략
문헌검색 데이터베이스 및 검색어
검색기간은 2008년 1월부터 2017년 12월까지의 10년 간 온라인 데이터에 등록된 논문이었다. 해외데이터베이스 는 Pubmed, Medline Complete(EBSCOhost)를 이용 하였고, 국내는 국회도서관(national assembly library of Korea)을 이용하였다. 검색어는 동일하게 (dysphagia OR “deglutition disorder” OR “swallowing disorder”) AND (stroke OR Apoplexy OR CVA OR “Cerebrovascular accident” OR “Cerebrovascular apoplexy” OR “vascular accident”) AND (treatment OR therapy OR rehabilitation) 으로 사용하였다.
포함기준 및 배제기준
성인 뇌졸중환자의 연하장애 치료에 대한 효과를 보고한 연구, 한국어 및 영어로 쓰인 논문, 전문 보기가 가능한 연구, 무작위 통제 실험연구 및 유사실험 연구를 포함기준 으로 정하였다. 반면, 고찰논문과 작업치료사들이 임상에서 사용하지 않는 경두개 직류자극기(transcranial Direct Current Stimulation; tDCS), 경두개 자기자극기(repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation; rTMS), 인두 전기 자극기(Pharyngeal Electrical Stimulation; PES), 기능적 자기 자극기(Functional Magnetic Stimulation; FMS)를 이용하여 치료한 연구는 제외하였다.
3문헌선택과정
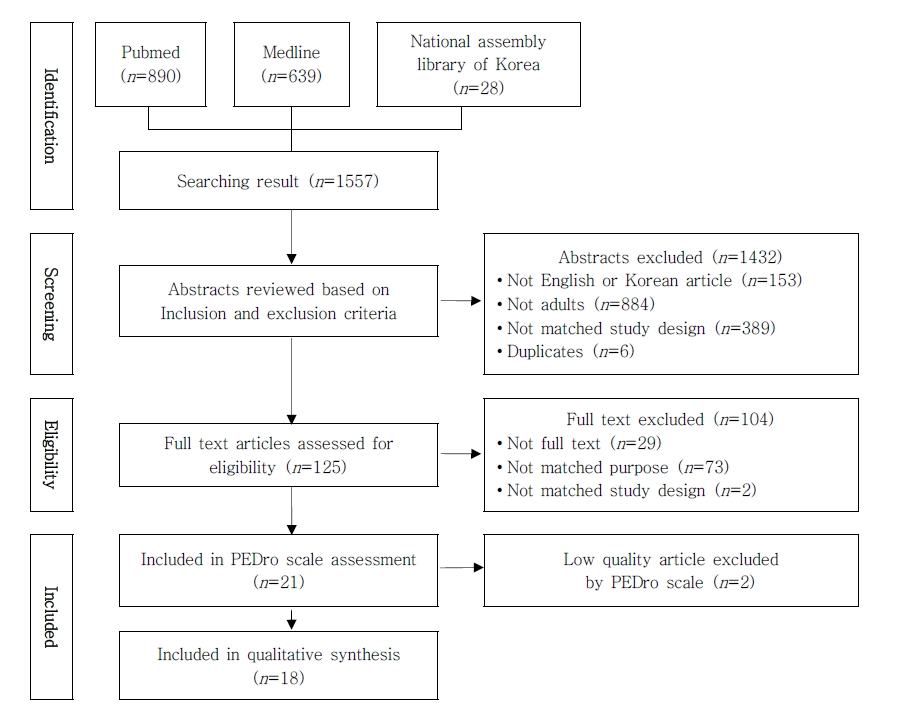
문헌의 수집과 선별은 2명의 저자가 개별적으로 검토 하여 진행하였다. 의견이 일치하지 않는 경우에는 의견 이 일치하도록 자료의 선정기준과 연구를 재검토하여 합 의하였다. 자료는 PRISMA(Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) 흐름 도를 이용하여 수집하고 분석하였다(Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, & Altman, 2009). 1차 초록 검토를 통하여 한글 및 영어가 아닌 경우, 대상자가 아동인 경우, 무작위 통제 실험연구 및 유사실험 연구가 아닌 경우, 검색이 중 복된 문헌인 경우는 제외하였다. 최종적으로 원문을 검 토하여 무작위 통제 실험연구 및 유사실험 연구가 아닌 경우, 연구의 목적이 적합하지 않은 경우를 제외하였다. 포함기준을 만족하는 21편의 문헌이 선별되었고, 추가 로 PEDro scale이 3점 이하인 문헌은 제외시켜서 최종 18편의 문헌을 선별하였다(Figure 1).
4문헌의 질 평가
Physiotherapy Evidence Database(PEDro) scale을 사용하여 최종적으로 선별된 문헌의 질을 평가하였다. PEDro scale은 문헌에 대한 일정 수준의 외적타당도와 내 적타당도를 제공하여 치료법의 질적 수준을 평가할 수 있 으므로 재활의학문헌에서 폭넓게 사용되는 도구이다 (Maher, Sherrington, Herbert, Moseley, & Elkins, 2003). 총 11항목으로, 각 항목에 해당하는 경우는 1점, 해 당하지 않거나 불확실한 경우는 0점이다. 총점은 10점으 로, 1번 항목을 제외하고 2번에서 11번까지 항목의 합이다 (Maher et al., 2003; Tooth, McCluskey, Hoffmann, McKenna, & Lovarini, 2005). 총점 3점 이하는 낮은 질적 수준, 4~5점은 중등도의 질적 수준, 6~8점은 높은 질적 수 준, 9~10점은 아주 높은 질적 수준을 의미한다(Foley, Teasell, Bhogal, & Speechley, 2003; Maher, 2000). 29 편의 문헌에 대하여 저자들이 각각 채점하였고, 의견이 불 일치한 경우에는 논의하여 합의점을 도출하였다. 총점이 3 점 이하로 낮은 질적 수준인 3편의 문헌을 제외하고 분석 을 실시하였다(Table 1).
Table 1
PEDro Scale for Researches
| No. | Author | Item | Total | Quality | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | ||||
| 1 | B low et al. (2008) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 8 | Good | ||
| 2 | Lim et al. (2009) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | Fair | ||||||
| 3 | Xia et al. (2011) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | Fair | ||||||
| 4 | Hong et al. (2012) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | Fair | |||||
| 5 | Park et al. (2012) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 9 | Excellent | |
| 6 | McCullough et al. (2012) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | Good | ||
| 7 | Park et al. (2012) | √ | √ | √ | √ | 3 | Poor | |||||||
| 8 | Nakamura et al. (2013) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | Fair | |||||
| 9 | Sun et al. (2013) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | Fair | |||||
| 10 | Rofes et al. (2013) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | Excellent | ||
| 11 | Jeong et al. (2014) | √ | √ | √ | √ | 9 | Poor | |||||||
| 12 | Toyama et al. (2014) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 3 | Good | ||
| 13 | Huang et al. (2014) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 8 | Fair | |||||
| 14 | Azola et al. (2015) | √ | √ | √ | √ | 5 | Poor | |||||||
| 15 | Jung (2015) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 3 | Good | ||||
| 16 | Zhang et al. (2016) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 6 | Good | ||
| 17 | Park et al. (2016) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 8 | Good | |||
| 18 | Park et al. (2016) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | Good | |||
| 19 | Hegland et al. (2016) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 7 | Fair | ||||||
| 20 | Kim et al. (2017) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 4 | Excellent |
| 21 | Koyama et al. (2017) | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 10 | Excellent | |
[i]
Item 1: Eligibility criteria were specified (not scored).
Item 2: Subjects were randomly allocated.
Item 3: Allocation was concealed.
Item 4: The groups were similar at baseline regarding the most important prognostic indicators.
Item 5: There was blinding of all subjects.
Item 6: There was blinding of all therapists who administered the therapy.
Item 7: There was blinding of all assessors who measured at least one key outcome.
Item 8: Measures of at least one key outcome were obtained from more than 85% of the subjects initially allocated to groups.
Item 9: Data for at least one key outcome was analyzed by intention to treat .
Item 10: The results of between-group statistical comparisons were reported for at least one key outcome.
Item 11: The study provided both point measures and measures of variability for at least one key outcome.
연구 결과
1분석대상 논문의 특성
최종분석의 대상이 된 논문은 18편이었다. 연구에 참 여한 대상자수는 14명에서 120명이었고, 2008년 연구 1편, 2009년 연구 1편, 2011년 연구 1편, 2012년 연구 3편, 2013년 연구 3편, 2014년 연구 2편, 2015년 연구 1편, 2016년 연구 4편, 2017년 연구 2편으로 2016년 연구가 가장 많았다. 18편의 논문에서 연하장애에 적용 된 치료방법은 총 14가지였다. 재활치료기법을 적용한 연구 7편, 신경근 전기자극과 전통적 연하장애치료를 병 합한 연구 6편, 신경근 전기자극만을 적용한 연구 1편이 었다. 언급된 대상자들의 증상은 연하장애 7회, 인두기 연하장애 3회, 구강인두기 연하장애, 하인두의 잔여물, 혀의 근력 약화 각 2회, 흡인과 침습, 머리조절, 후두 상 승 감소, 상부식도괄약근 개방 감소, 삼킴반사 지연, 중등 도 연하장애, 경도 연하장애, 최소 삼킴 기능 손상, 구강- 인두 연하장애, 기침, 식사시간 지연, 비강 역류, 삼킴 어 려움이 각 1회 순으로 언급되었다. 병변 부위는 대뇌반구 와 뇌간 부위가 혼합된 연구 10편, 대뇌피질 부위 연구는 6편, 뇌간 부위 연구는 1편이었고, 병변 부위가 기록되지 않은 연구가 1편이었다. 발병 시기는 급성과 만성이 혼합 된 연구 13편, 3개월 미만의 급성기 환자를 대상으로 한 연구 3편, 3개월 이상의 만성기 환자를 대상으로 한 연구 1편이었고, 발병 시기가 기록되지 않은 연구가 1편이었 다(Table 2).
Table 2
Characteristics of Analyzed Studies
| No. | Authors | Symptom | Lesion onset | Treatment | Effect | Sample size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | B low et al. (2008) | 1) Dysphagia |
1) hemisphere 2) More than 3 months |
1) NMES | 1) Same as the effect of traditional treatment | 25 |
| 2 | Lim et al. (2009) | 1) Dysphagia | 1) Variable |
1) NMES-S + TTS 2) 1h at a frequency of 5 per week |
1) Improving swallowing or aspiration severity | 28 |
| 3 | Xia et al. (2011) | 1) Dysphagia | ー | 1) NMES + TT | 1) Alleviate post-stroke dysphagia 2)Improving patients quality of life | 120 |
| 4 | Hong et al. (2012) |
1) Pharyngeal dysphagia 2) Aspiration/penetration |
1) Variable |
1) Shaker exercise 2) 30min/day, 5days/week, 6weeks |
1) Epiglottis residue 2) Laryngeal elevation 3) Pharyngeal transit time 4) Aspiration 5) Diet level |
19 |
| 5 | Park et al. (2012) | 1) Dysphagia |
1) Variable 2) More than 1 month |
1) NMES-I + effortful swallow 2) 20min/session, 4 weeks, total 12 sessions |
1) Increased laryngeal excursion | 18 |
| 6 | McCullough et al. (2012) |
1) Pharyngeal dysphagia 2) Reductions hyolaryngeal elevation 3) Reductions UES opening 4) Residue in the pharynx |
1) Variable 2) 6 weeks~ 22 months |
1) Mendelsohn maneuver 2) 1 session 45~60min, 2 sessions/day, 2 weeks |
1) Duration of superior and anterior hyoid movement | 18 |
| 7 | Nakamura et al. (2013) |
1) Delayed swallowing reflex 2) Dysphagia |
1) Supranuclear (n=15) 2) Nuclear(n=9) |
1) Ice massage 2) Daily swallowing training |
1) Shortened triggering the swallowing reflex 2) Immediate effect on triggering a swallow response(more effect in supranuclear lesions than nuclear lesions) |
24 |
| 8 | Sun et al. (2013) | 1) Moderate to severe dysphagia |
1) Variable 2) More than 3 weeks |
1) NMES-M + FEES 2) 50 min/day, 3 days/week, 4 weeks total 12 sessions 3) Additional TT 4) 1 h/day, 5 days/week, 2-3 weeks, total 12 sessions |
1) Improved swallowing functions | 32 |
| 9 | Rofes et al. (2013) | 1) Pharyngeal dysphagia |
1) Variable 2) More than 6 months |
1) NMES-S 2) NMES-M 3) 10 days, 1 h/day |
1) Improved swallow response and safety (NMES-S and NMES-M) 2) Efficacy of swallow (NMES-M) 3) Safe and effective therapy for chronic dysphagia patients |
20 |
| 10 | Toyama et al. (2014) | 1) Pharyngeal dysphagia | 1) Hemisphere |
1) NMES-M + TT 2) 40min/day, 5 days/week, 8 weeks |
1) Increased hyoid bone and larynx excursion 2) Improved swallowing functions (especially pharyngeal function) |
26 |
| 11 | Huang et al. (2014) | 1) Dysphagia |
1) Hemisphere 2) Less than 3 months |
1) NMES-M + TT 2) 60 min/session, 3 sessions/week, 10 sessions of NMES |
1) More effective in solid diet and large food | 29 |
| 12 | Jung (2015) | 1) Dysphagia |
1) Variable 2) Less than 1 year |
1) TT + THM 2) 30 min/day, 5 days/week, 8 weeks, 40 sessions |
1) Improved swallowing functions 2) Reducing pain during swallowing |
28 |
| 13 | Zhang et al. (2016) |
1) Oropharyngeal dysphagia 2) Water choke to cough 3) Prolonged eating time 4) Difficulty swallowing 5) Nasal regurgitation |
1) Medullary infarction 2) Less than 4 weeks |
1)NMES-S + TT 2) NMES-M + TT 3) 20 min/session, 2session/day, 5day/wk, more than 4 weeks |
1) Recovery from dysphagia 2) Improves quality of life 3) More effect in NMES-S than NMES-M |
82 |
| 14 | Park et al. (2016) | 1) Dysphagia |
1) Variable 2) 17~49 wks |
1) EMST 2) 25breaths(5breaths X 5sets)/day, 5 days/wk |
1) Stimulating activity in the suprahyoid muscle group 2) Reduction of penetration aspiration |
27 |
| 15 | Park et al. (2016) | 1) Mild dysphagia |
1) Hemisphere 2) 30~42 mon |
1) NMES + effortful swallow 2) 30 min/session, 5 sessions/week, 6 weeks |
1) Greater improvements in hyoid displacement 2) Oropharyngeal swallowing function (especially pharyngeal function) |
50 |
| 16 | Hegland et al. (2016) | 1) Minimally impaired swallow function |
1) Hemisphere 2) 3~24 mon |
1) EMST 2) 25breaths(5breaths X 5sets)/day, 5 days/wks (home program) |
1) Improving expiratory muscle strength 2) Improving Reflex cough strength 3) Improving Urge to cough |
14 |
| 17 | Kim et al. (2017) |
1) Oropharyngeal dysphagia 2) Tongue muscle weakness |
1) Hemisphere 2) 0~10 mon |
1) TPRT 2) 5days/week, 4 weeks, 30 sessions |
1) Increasing tongue muscle strength 2) Improving oropharyngeal swallowing function |
35 |
| 18 | Koyama et al. (2017) | 1) Hypopharyngeal residue |
1) Variable 2) 6~9 weeks |
1) MJOE 2) 4sets/day, 5 sessions/week, 6weeks |
1) Increased hyoid bone | 16 |
[i] EMST: Expiratory muscle strength training, FEES: Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing, MJOE: Modified Jaw Opening Exercise, NMES: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation, NMES-I: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation-Infrahyoid muscle stimulation, NMES-M: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation-Motor level stimulation, NMES-S: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation-Sensory level stimulation, THM: Tongue-Holding Maneuver, TPRT: Tongue-to-Palate Resistance Training, TT: Traditional Therapy, TTS: Thermal Tactile Stimulation, UES: Upper Esophageal Sphincter
2치료방법의 분류
치료효과에 따른 분류
총 14가지의 치료방법 중 인두기에 효과를 보인 치료 가 14건, 구강기에 효과를 보인 치료와 식이 단계에 효과 를 보인 치료가 각각 1건이었다(Table 3).
Table 3
Classification According to the Effect of Treatment
[i] EMST: Expiratory muscle strength training, FEES: Fiberoptic Endoscopic Evaluation of Swallowing, MJOE: Modified Jaw Opening Exercise, NMES: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation, NMES-I: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation-Infrahyoid muscle stimulation, NMES-M: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation-Motor level stimulation, NMES-S: Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation-Sensory level stimulation, THM: Tongue-Holding Maneuver, TPRT: Tongue-to-Palate Resistance Training, TT: Traditional Therapy, TTS: Thermal Tactile Stimulation, UES: Upper Esophageal Sphincter
증상에 따른 분류
연하장애의 임상 증상인 혀 근력 약화, 삼킴반사 지연, 후두개 잔여물, 설골과 후두의 앞위쪽 움직임 저하, 음식 덩이의 인두통과시간 지연, 흡인과 침습, 삼킬 때의 통증, 구강인두 기능저하, 상부식도괄약근 개방 지연과 식이 단계에 따라 치료방법을 분류하였다. 가장 많은 치료방 법이 적용된 증상은 구강인두 기능저하로 총 7가지의 치 료 방법이 제시되었다. 설골과 후두의 앞-위쪽 움직임 저하는 6가지, 흡인과 침습은 4가지, 삼킴반사 지연은 3 가지, 혀의 근력 약화, 후두개 잔여물, 음식덩이의 인두통 과시간 지연, 그리고 삼킬 때의 통증은 각각 1가지의 치 료 방법이 제시되었다(Table 4).
Table 4
Classification of Treatment Methods According to Clinical Symptoms
고 찰
본 연구는 뇌졸중 환자를 대상으로 한 최근의 연하재 활치료에서 병변, 발병 시기오 같은 임상 치료의 효과에 크게 영향을 주는 요인들이 어떻게 반영되고 있는지를 살펴보고자 하였다. 또한 제시된 치료 방법들을 치료의 효과와 각 연하장애 증상별로 재정리하여, 연하재활치료 를 할 때 환자의 특성에 적합한 효과적인 치료 방법을 선 택할 수 있는 근거를 확보하고자 하였다. 본 연구에서는 문헌검색과정에서 경두개 직류자극기, 경두개 자기자극기,인두 전기자극기, 기능적 자기자극기와 관련된 연구는 제외하였다. 이는 작업치료사들이 임상에서 현실적으로 접하기가 어렵고, 즉시 적용할 수 있는 연하재활치료 방 법들을 살펴보고, 그 효과를 정리하는데 불필요하기 때 문이다. 또한 신뢰도 있는 정보제공을 위하여 무작위 대 조 연구와 그에 준하는 임상실험 연구들을 선별하였으며, 문헌의 질을 평가하기 위하여 PEDro scale을 사용하여 질적 수준을 측정하였다. 본 연구는 치료 방법에 대한 체 계적 고찰연구이지만, 뇌졸중 환자의 특성에 따른 연하 재활 치료의 효과를 확인하고자 하였으므로 PEDro scale을 선택하여 적용하였다.
본 연구에서 검토된 연구에서는 뇌졸중 병변 부위는 대뇌반구와 뇌간 부위가 혼합된 연구 10편, 대뇌피질 부 위 연구는 6편, 뇌간 부위 연구는 1편이었고, 병변 부위 가 기록되지 않은 연구가 1편이었다. 대뇌반구와 뇌간이 혼합된 연구에서는 각 병변이 실험군과 대조군에 모두 혼합되었다. 이는 대뇌 피질을 병변으로 한 연구에서도 동일했다. 즉, 병변부위가 세부적으로 통제되지 않았고, 포괄적으로 ‘대뇌반구’ 및 ‘뇌간’으로만 표기되어 있다. 다만 뇌간의 병변을 대상으로 한 연구에서는 숨뇌 로 구체적인 병변이 표기되어 있었다.
발병 시기는 급성과 만성이 혼합된 연구 13편, 3개월 미만의 급성기 환자를 대상으로 한 연구 3편, 3개월 이상 의 만성기 환자를 대상으로 한 연구 1편이었고, 발병 시 기가 기록되지 않은 연구가 1편이었다. 발병 시기는 뇌졸 중 환자의 연하재활치료 효과에 매우 큰 영향을 미치는 요인임에도 불구하고 급성과 만성이 혼합된 치료가 13 편이나 되었다. 급성기 환자를 대상으로 한 3편의 연구 중에서 병변 부위가 세부적으로 통제된 연구는 1편이었 다. 이 연구에서는 급성기 숨뇌 병변의 뇌졸중 환자들의 구강인두 연하장애, 물을 마실 때 기침, 식사시간 지연, 삼킴의 어려움, 코로의 역류에 대하여 감각자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료와 전통적 연하재활치료, 운동자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료와 전통적 연하재활치료를 4주 동안 주 5회, 하루 20분씩 2회를 시행하여 연하기능 을 회복하고, 삶의 질이 향상되었다. 특히 급성기 숨뇌 병변 환자의 경우 감각자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료 와 전통적 연하재활치료를 병행했을 때 더 좋은 치료 효 과를 보였음을 알 수 있었다.
최근 연구에서 제시되고 있는 치료방법들을 치료법의 효과를 기준으로 살펴본 결과, 총 14가지의 치료방법 중 인두기에 효과를 보인 치료가 14건, 구강기에 효과를 보 인 치료와 식이 단계에 효과를 보인 치료가 각각 1건이었 다. 이러한 결과는 연하재활치료에 사용되고 있는 새로 운 기법들이 대부분 인두기에 집중되어 있기 때문이다. 인두기의 기능 회복을 극대화시키기 위하여 새로운 기법 과 함께 병행되는 전통적 연하재활기법은 인두기의 기능 회복과 관련이 큰 노력 삼킴법이었다. 상부식도괄약근의 개방에 효과를 보인 치료법은 본 연구에서 분석한 논문 에서는 찾을 수 없었다. 목뿔아래 근육에 운동자극 수준 의 신경근 전기자극을 주며 노력삼킴을 병행한 치료와 shaker 운동이 상부식도괄약근의 개방에 효과가 있었으 나, 유의하지 않았다.
연하장애의 임상 증상에 따라 치료법을 분류한 결과, 구강인두 기능저하에 대하여 총 7가지의 연하재활 치료 방법이 제시되었다. 이는 포괄적인 증상에 대하여 효과 가 있는 여러 가지 치료들이 모두 해당되었기 때문이다. 이는 아직까지 대상자의 증상에 대한 세부적이고 정확한 원인을 찾아내어, 그에 알맞은 구체적인 연하재활치료가 시행되지 않고 있음을 짐작할 수 있다. 다만, 세부적인 연구 결과로, 구강인두 기능저하를 보이는 숨뇌 병변의 뇌졸중 환자에게는 감각자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치 료가 효과적이었고, 대뇌 반구 병변의 뇌졸중 환자에게 는 운동자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료가 효과적임을 확인할 수 있었다. 목뿔뼈와 후두의 앞-위쪽 움직임 저 하에 대해서는 총 6가지의 치료 방법이 제시되었다. 이는 대부분의 치료가 목뿔뼈와 후두를 거상시키는 근육들에 대한 신경근 전기자극치료에 대하여 많은 연구가 이루어 졌기 때문이다. 특히 분류 결과를 토대로 신경근 전기자 극이 목뿔뼈와 후두를 효과적으로 거상시키기 위하여 병 행되는 치료로 노력 삼킴이 추천되었고, shaker 운동, 멘 델슨 메뉴버, 수정된 턱관절 개방 운동이 신경근 전기자 극과 병행하여 제공된다면, 치료의 효과를 더욱 강화시 킬 수 있을 것이라 판단된다.
본 연구에서는 병변, 발병 시기와 같은뇌졸중 환자의 연하재활치료에 크게 영향을 주는 요인들이 어떻게 반영 되고 있는지 살펴보고자 하였다. 그러나 대부분의 연구 들이 이와 같은 중요한 요인을 통제하지 않고 있었기 때
문에 이러한 요인이 어떤 영향을 미치는지를 확인할 수 없었다. 그럼에도 불구하고 최근 연구들이 제시하고 있 는 치료 방법들을 치료 방법의 효과와 각 연하장애 증상 별로 재정리함으로써 급성기 뇌졸중 숨뇌 병변 환자에게 감각자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료와 전통적 연하재 활치료를 병행했을 때 효율적으로 치료할 수 있다는 것 을 알 수 있었다. 그리고 신경근 전기자극치료의 경우 구 강인두 기능저하를 보이는 숨뇌 병변의 뇌졸중 환자에게 는 감각자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료가 효과적이고, 대뇌 반구 병변의 뇌졸중 환자에게는 운동자극 수준의 신경근 전기자극치료가 효과적임을 확인할 수 있었다. 마지막으로 목뿔뼈와 후두를 효과적으로 거상시키기 위 하여 많이 사용되고 있는 신경근 전기자극의 효과를 극 대화하기 위해서는 이러한 목적으로 사용되고 있는 노력 삼킴, shaker 운동, 멘델슨 메뉴버, 수정된 턱관절 개방 운동과 함께 병행하여 제공되면 효과적일 것임을 알아낼 수 있었다.
체계적 고찰을 시행하는데 있어서 모든 문헌을 포함해 야 하지만, 저자의 특성상 한글과 영어 논문에 한하여 시 행한 점, 수많은 데이터베이스 중에서 4가지만을 선택적 으로 검색한 점, 연하장애 관련 자료에 대한 수기검색은 하지 않았다는 점, 학위논문은 제외하였다는 제한점이 있었다. 또한 임상에서 적용되기 시작하는 기법들에 대 해서 현재 작업치료사들이 거의 사용하고 있지 않다는 이유로 몇몇 유용한 연하재활치료 방법을 보고에서 제외 하였다. 그럼에도 PRISMA 체크리스트 및 흐름도를 사 용하여 엄격한 기준으로 문헌을 검색하고 보고하였다는 점은 의미가 있다.
최근의 연하재활치료 방법을 치료 방법의 효과와 각 연하장애 증상별로 정리하여 제시한 본 연구를 참고한다 면, 임상에서 작업치료사들이 환자의 연하장애 증상과 그에 가장 적합한 치료방법을 선택하고, 그 치료방법의 효과를 예상하며, 효율적으로 치료할 수 있을 것이다.